Osteochondrosis is a degenerative destruction of the spine, which includes the defeat of the vertebrae, joint devices, league devices and intervertebrate discs. This disease is quite evenly in all countries - 45-85% of the population has this disease. The beginning of osteochondrosis occurs in patients over 30-35 years of age, but cases of earlier appearance of the disease are also known. Men and women are approximately the same frequency.
Reasons
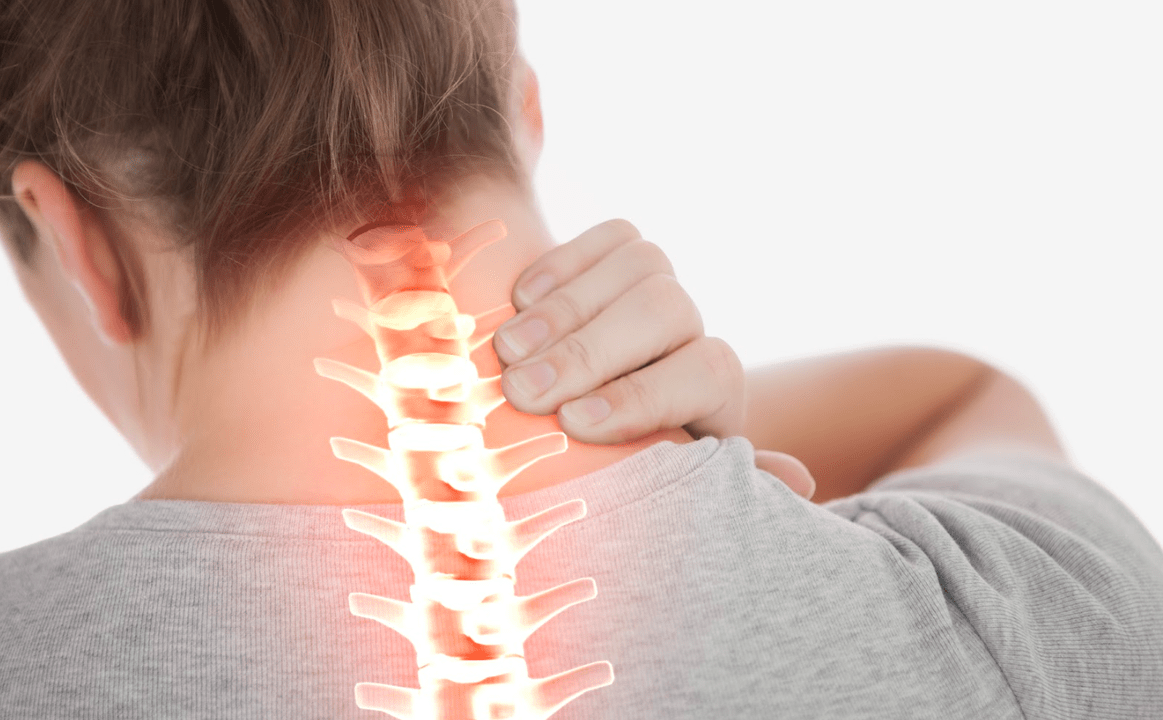
There is no uniform reason for the development of osteochondrosis. There are many prone reasons -there are factors. The most important are:
- Spine injuries (fractures, bruises, dislocations);
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Foot diseases that cause spinal overload - which includes flat legs, deformation of the foot, with the feet;
- Wearing tight and unpleasant shoes for a long time (also causing overload of the spine);
- Overweight and obesity;
- Age -related changes;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Athletes who suddenly leave their training and classes;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Spine curvature (kyphosis, lordosis, skoliosis);
- Professional characteristics - weight lifting, frequent turns and body jerks, working in an unpleasant position;
- Frequent and extended hypothermia;
- Voltage;
- A special climate, both at the place of residence and in the workplace - low air temperature and high humidity.
If they are exposed to one or more causal factors, the disease begins. Usual to divide into four main sections:
- The first stage- The amount of moisture in the core of the intervertebral disk decreases, becomes more ski, and the distance between the vertebrae is reduced. The cartilage is covered with smaller cracks.
- The second stage- Due to the reduction of the distance between the vertebrae, the vertebrae is a muscle and ligasic device. This leads to abnormal mobility of the spinal bodies to move.
- The third stage- Due to the progressive processes of the spine, the clamping of the intervertebral discs (prominence), the vertebrae are subluxation.
- The fourth stage- Bone spikes (osteophytes) appear between the vertebrae to eliminate the mobility of the vertebrae and prevent dislocations. Over time, there are so many that the vertebrae involved completely lose their mobility. In this case, the trauma of the blood vessels and nerves passes through the vertebrae and leaves the spinal column.
In the first and last stages of clinical manifestations (pain), the patient has no patient.
Classification
Osteochondrosis has many classifications. Each doctor chooses the most acceptability. The following classifications are most often used:
Classification of a spine defeat:
- Cervix osteochondrosis;
- Chest osteochondrosis;
- Lumbar osteochondrosis;
- Coronation of osteochondrosis;
- Extensive (common) osteochondrosis - affects 2 or more spines.
Classification with the degree of change in intervertebral disc (radiological stages):
- Stage 0 - no album change;
- Section 1 - minor changes including maximum internal tears;
- Stage 2 - severe changes on the plate while retaining the outer surface;
- Section 3 is completely influenced by the entire disk (cracks spread to the outer surface and the disc from the vertebrae's body, etc. ).
Classification with clinical manifestations and the degree of operation of the impaired spine:
- Section 1 - The function of the spine does not change, the patient feels slight pain in the injury;
- Stage 2 - the function of the spine is disturbed (the subluxes of the spinal bodies occur, the disc protrusion, the nerve clamping), the pain increases in the destructive location;
- Section 3 - the spine is deformed, the hernia of the intervertebral discs, the severe pain;
- Stage 4 - The patient is difficult to move, the mobility of the spine is reduced and the pain during the slightest movement. The patient has disabilities.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis

Symptoms of osteochondrosis depend on the damage to the spine and the degree of disorders that occur.
The following symptoms are characterized by the extended clinical picture of the cervical spine osteochondrosis:
- Violation of visual acuity;
- Dizziness;
- Tinnitus;
- Blink in front and appearance of colored spots;
- Hearing loss;
- Headache in the chest, temporal and parietal regions, enhancing the cervical spine;
- Loss of awareness;
- Snoring;
- Hoarse the sound or its weakening;
- Loss of numbness and sensitivity on the skin of the face, neck and hands;
- Dental destruction;
- Blood pressure body.
The following symptoms are characterized by osteochondrosis of the chest spine:
- The pain of the heart that lasts for a long time is painful or press, often sharp, sewing, sharp, patients can show a specific point of pain;
- Numbness of the skin in the chest, abdomen and back;
- Spine pain, especially between blades, highly expressed;
- Pain when he raises his hands;
- Pain with sharp and deep breath, then connect later during exhalation;
- Pain, discomfort and difficulty in the body in any direction.
The following symptoms are characterized by osteocondrosis of lumbar and sacred spine:
- Pain in the area of lumbar and sacred spine (lumbalgia), which can give one or both legs, increasing any movement of the spine in the affected area;
- The legs freeze at comfortable temperatures in other parts of the body;
- Almost constant tension in the back muscles, especially in the lumbar region;
- Numbness, climbing goose pumps and tingling on the skin and buttocks;
- Varicose veins on the legs;
- Violation of men's efficiency;
- Increased sweating;
- Pale skin of the skin;
- Irregular menstruation in women.
In the case of longer and neglected osteochondrosis, when the vertebrae are merged with each other, the patient is only worried about the impossibility of the spine, the pain is usually reduced or completely left.
Diagnosis
Above all, the doctor conducts a survey and examination of the patient, creating a preliminary diagnosis. Further test methods are assigned to confirm. In the case of osteochondrosis, these are only instrumental because laboratory (tests) do not show confirmation changes.
The main diagnostic methods are as follows:
- X -Gay test. It allows the determination of the damage to the vertebrae, their location and the definition of bone formations. Indirect methods to determine the condition of bone channels and intervertebral discs;
- Computer tomography (CT). Allows you to determine the condition, structure and shape of the intervertebral discs, deformation of the vertebrae, and compression of nerve endings and roots;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Allows for minor infringements of the spine and prescribes it in cases where contradictory issues continue to be the post of CT;
- Ultrasound procedure. Allows the degree of blood flow to identify the spinal cord and other organs;
- Myelography. Method of spinal radiography with contrast medium. Allows the identification of intervertebral hernia.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment methods are primarily used in the treatment of osteochondrosis. In this case, the approach to individual patients should be individual and complex. Conservative treatment methods can be divided into 4 main groups:
- Drug treatment;
- Physiotherapy;
- Spa treatment;
- Diet (basics of proper nutrition).
Osteochondrosis drug treatment
Medicines used to treat osteochondrosis should be used during the aggravation period. These contribute to the reduction of symptoms and also affect some causal factors for the development of the disease. Main groups of medicines used to treat osteochondrosis:
- Nsaid. Non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs have anesthetic, anti -inflammatory effects and reduce the increased temperature of the tissues of the spine and its structure. In the case of prominent symptoms, the first days of worsening of the disease are prescribed in the form of injections. The frequency of use is 1-2 times a day. They then, if necessary, switch to tablet forms of 10-30 days of treatment. The frequency of entry is 1-4 times a day. In addition, the ointment or cream with tablets and injections is applied to the skin 1-3 times a day in the spine.
- Musorelaxants. Preparations of this group perform a great deal of cope with increased muscle tone, relaxation of the transversely broken muscle fibers and facilitating the patient's condition. On average, about 1 month during treatment. With severe symptoms, the treatment begins with injection forms of drugs. Dosage is minimal, gradually increasing until the therapeutic effect is reached, then gradually reducing total resignation.
Additional additional groups are used as additional medicines:
- Vitamins. Accelerate tissue recovery processes, normalize nerve conductivity, accelerate metabolism, etc. Almost always these drugs for osteochondrosis are prescribed injections and courses for 10 days. These are vitamins B1, B2, B6, E.
- Blood preparations. These drugs normalize blood flow in veins and arteries, restore blood vessels and restore metabolism. Most often, forms of tablet release are used. The treatment with these agents is 1-3 months. In extreme cases, the drug injection is possible in the first 5-10 days, transitioning to the subsequent tablets.
- Glucocorticosteroids. They have anti -inflammatory, decongestant effects and improve the work of NSAIDs and muscle relaxants. Depending on the severity of the patient's condition, they are prescribed intramuscularly or in the form of intra -infalactic injections or in the form of tablets needed for oral administration. The course of treatment is selected separately -for several days for several weeks. The abolition of the drug should be done with a gradual decrease in the dose.
- Biogenic stimulants. Accelerate metabolism, stimulate tissue recovery, reduce tissue inflammation and swelling, and much more. It is most often used in the form of injection and slightly less often in the form of tablets or other oral forms. Treatment can be between 1 week and 2-3 months, depending on the severity of the disease.
Physiotherapy treatment of osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy measures combined with drugs allow for acceleration of recovery processes and extend the period of remission when used outside the aggravation. There are many physiotherapy methods and most of them are well practiced in the treatment of osteochondrosis:
- Electrophoresis. Depending on the drug used in the procedure, an analgesic effect is obtained. Metabolism has improved and the normalization of blood flow in the affected tissues.
- Acupuncture (acupuncture). With the help of special finest needles and the effects of active points on the patient's skin, they achieve an analgesic effect, stimulate healing and metabolism, and reduce inflammation.
- Magnetic therapy. Reduces pain, swelling and inflammation of the tissues, accelerates nerve conductivity, normalizes metabolism
- Hand therapy. Mobility is restored in the spine joints and the pain syndrome is reduced.
- Massage. It normalizes muscle tone, eliminates back pain, restores nerve conductivity.
- Practical therapy. Restoring spine mobility, reduction in pain, restoring the usual lifestyle, strengthening the muscular frame of the back, relaxation of the back muscles, accelerating metabolism.
- Adhesion of the spine. The mobility of the spine is restored, prevents the disease from progressing and developing complications and impenetting.
- Laser therapy. It improves blood supply, stimulates tissue regeneration, reduces pain and inflammation, and reduces spine swelling.
- Thermotherapy. Anesthetic effect, blood flow and normalization of lymphatic through blood vessels, decrease in inflammation in tissues, acceleration of cartilage recovery.
- Almost (peloid therapy). Reduces spine pain, reduces muscle cramps, slightly reduces inflammation, improves blood supply and metabolism.
A patient can be prescribed for 1 physiotherapy event and their complex. This depends on the severity of the process of osteochondrosis and the accompanying pathologies. The average duration of treatment is 10-15 days. We recommend that you repeat 3-4 times during the year. This can reduce the frequency of aggression and the speed of osteochondrosis progression several times.























